Area Definitions
The FBI’s Uniform Crime Reporting (UCR) Program collects crime data and supplemental information that make it possible to generate a variety of statistical compilations, including data presented by reporting areas. These statistics provide data users with the opportunity to analyze local crime data in conjunction with data for areas of similar geographic location or population size. The reporting areas that the UCR Program uses in its data breakdowns include community types, population groups, and regions and geographic divisions. For community types, the UCR Program considers proximity to metropolitan areas using the Office of Management and Budget’s (OMB’s) designations. (Generally, sheriffs, county police, and state police report crimes within counties but outside cities; local police report crimes within city limits.) The number of inhabitants living in a locale (based on the U.S. Census Bureau’s figures) determines the population group into which the program places it. Finally, in its geographic breakdowns, the UCR Program divides the United States into regions and divisions.
Community types
In order to assist data users who wish to analyze and present uniform statistical data about metropolitan areas, the UCR Program uses reporting units that represent major population centers. The program compiles data for these areas according to three types of communities:
1. Metropolitan Statistical Areas (MSAs)—Each MSA contains a principal city or urbanized area with a population of at least 50,000 inhabitants. MSAs include the principal city; the county in which the city is located; and other adjacent counties that have, as defined by the OMB, a high degree of economic and social integration with the principal city and county as measured through commuting. In the UCR Program, counties within an MSA are considered metropolitan. In addition, MSAs may cross state boundaries.
Some presentations in this publication refer to Metropolitan Divisions, which are subdivisions of an MSA that consists of a core with “a population of at least 2.5 million persons. A Metropolitan Division consists of one or more main/secondary counties that represent an employment center or centers, plus adjacent counties associated with the main county or counties through commuting ties,” (Federal Register 65 [249]). Also, some tables reference suburban areas, which are subdivisions of MSAs that exclude the principal cities but include all the remaining cities (those having fewer than 50,000 inhabitants) and the unincorporated areas of the MSAs.
Note: Because the elements that comprise MSAs (particularly the geographic compositions) are subject to change, the program discourages data users from making year-to-year comparisons of MSA data.
2. Cities Outside MSAs—Ordinarily, cities outside MSAs are incorporated areas.
3. Nonmetropolitan Counties Outside MSAs—Most nonmetropolitan counties are
composed of unincorporated areas.
Community types are further illustrated in the following table:
|
Metropolitan |
Nonmetropolitan |
|
Principal Cities (50,000+ inhabitants) |
Cities outside Metropolitan Areas |
|
Suburban Cities |
|
|
Metropolitan Counties |
Nonmetropolitan Counties |
Population groups
The UCR Program uses the following population group designations:
|
Population Group |
Political Label |
Population Range |
|
I |
City |
250,000 and more |
|
II |
City |
100,000 to 249,999 |
|
III |
City |
50,000 to 99,999 |
|
IV |
City |
25,000 to 49,999 |
|
V |
City |
10,000 to 24,999 |
|
VI1,2 |
City |
Less than 10,000 |
|
VIII (Nonmetropolitan County)2 |
County |
N/A |
|
IX (Metropolitan County)2 |
County |
N/A |
1Includes universities and colleges to which no population is attributed.
2Includes state police to which no population is attributed.
Individual law enforcement agencies are the source of UCR data. The number of agencies included in each population group may vary from year to year because of population growth, geopolitical consolidation, municipal incorporation, etc. In noncensus years, the UCR Program estimates population figures for individual jurisdictions. (A more comprehensive explanation of population estimations can be found in the Methodology.)
The table below shows the number of agencies within each population group that were eligible to participate in the UCR Program for 2018:
|
Population Group |
Number of Agencies |
Population Covered |
|
I |
86 |
63,376,799 |
|
II |
227 |
33,687,261 |
|
III |
505 |
35,214,004 |
|
IV |
912 |
31,688,691 |
|
V |
1,925 |
30,656,148 |
|
VI1,2 |
9,841 |
26,428,671 |
|
VIII (Nonmetropolitan County)2 |
2,860 |
27,208,256 |
|
IX (Metropolitan County)2 |
2,225 |
78,907,604 |
|
Total |
18,586 |
327,167,434 |
1Includes universities and colleges to which no population is attributed.
2Includes state police to which no population is attributed.
Regions and divisions
The map below illustrates the four regions of the United States along with their nine geographic divisions as established by the U.S. Census Bureau. The UCR Program uses this widely recognized geographic organization when compiling the nation’s crime data.
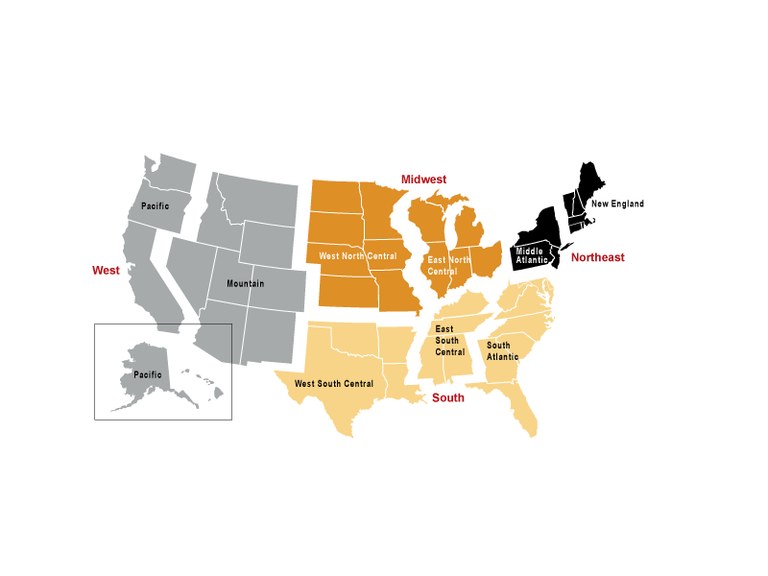
The following table lists the 50 states and the District of Columbia arranged according to the regions and geographic divisions of the United States.
NORTHEASTERN STATES
|
New England |
Middle Atlantic |
|
Connecticut |
New Jersey |
|
Maine |
New York |
|
Massachusetts |
Pennsylvania |
|
New Hampshire |
|
|
Rhode Island |
|
|
Vermont |
|
MIDWESTERN STATES
|
East North Central |
West North Central |
|
Illinois |
Iowa |
|
Indiana |
Kansas |
|
Michigan |
Minnesota |
|
Ohio |
Missouri |
|
Wisconsin |
Nebraska |
|
|
North Dakota |
|
|
South Dakota |
SOUTHERN STATES
|
South Atlantic |
East South Central |
|
Delaware |
Alabama |
|
District of Columbia |
Kentucky |
|
Florida |
Mississippi |
|
Georgia |
Tennessee |
|
Maryland |
West South Central |
|
North Carolina |
Arkansas |
|
South Carolina |
Louisiana |
|
Virginia |
Oklahoma |
|
West Virginia |
Texas |
WESTERN STATES
|
Mountain |
Pacific |
|
Arizona |
Alaska |
|
Colorado |
California |
|
Idaho |
Hawaii |
|
Montana |
Oregon |
|
Nevada |
Washington |
|
New Mexico |
|
|
Utah |
|
|
Wyoming |
|

